Security firm Sucuri says that, during the first three months of 2016, the company saw a large number of attacks targeting websites running on the WordPress CMS platform.
The company released yesterday its first-ever Website Hacked Report, in which it compiled statistics from over 11,485 compromised sites it was called upon to investigate.
As we expected, a large portion of these compromised websites were running on WordPress, the most successful CMS platform for the past five-six years.
Nearly four in five hacked websites were running WordPressMore precisely, Sucuri reveals that 78 percent of the total number of hacked websites it investigated were WordPress sites, with Joomla in a distant second, taking up only 14 percent of the data sample. Further, six percent were no-CMS websites, 5 percent were running Magento, and 2 percent were using Drupal.
Looking back at historical data the company collected in the past years, Sucuri says that Q1 2016 was a quiet period, with no visible spike in the number of infected websites in total, or for a certain platform.
Something like this happened last year, at the start of 2015, when the Shoplift Magento bug appeared, and hackers tried to exploit it starting day one.
It is because of this same bug that Magento is a highly sought-out target, seeing more attacks than Drupal, even if there are more Drupal sites online. In most cases, crooks who hack Magento sites go after credit card numbers collected through payment pages and don't bother with SEO spam or exploit kits, as is the case with hacked WordPress, Joomla, and Drupal sites.
Point of entry for most hacks was a vulnerable plugin, not the CMS coreAs for a breakdown of hacked WordPress sites, Sucuri says that a large part can be attributed to outdated plugins. There were minimal attempts to use vulnerabilities in the WordPress core itself, and crooks relied on WordPress' popularity and its large plugins and themes ecosystem to inflict their damage.
Sucuri says that, from all the compromised WordPress sites they analyzed, they found the intrusion point inside a vulnerable plugin. A quarter of these attacks can be attributed to three plugins: RevSlider, GravityForms, and TimThumb.
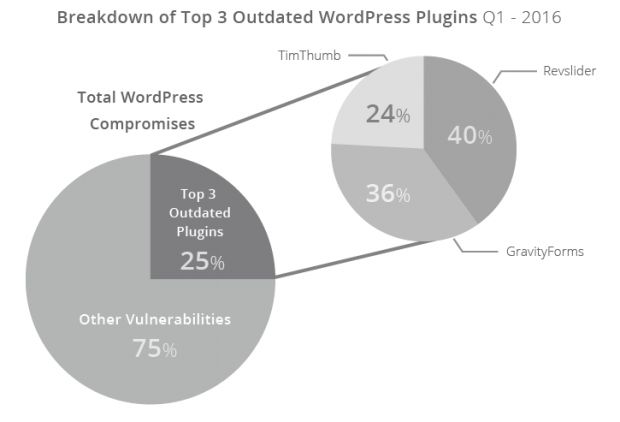
Three plugins are responsible for a quarter of WordPress hacking incidents
RevSlider is also the plugin suspected to be at the core of the Panama Papers data breach. What makes this statistic more mind-blowing is the fact that, for all three plugins, developers released security fixes more than a year ago. For TimThumb, the security fix was released four years ago, yet there are still WordPress sites using the plugin's vulnerable version.
This is because, as with RevSlider, there are a lot of developers that have embedded these plugins inside custom themes, usually commercial products available through theme marketplaces such as ThemeForest, Mojo Themes, and others.
Even if plugins can be deployed automatically with themes during the theme's installation, some developers have chosen to embed plugins within the theme's code so as to allow users to manage their content via a central theme control panel.
This kind of setup makes upgrading the plugin's code via the WordPress built-in plugin manager impossible, and theme developers need to re-issue themes with new plugin versions once every few months. Which, as you guessed it, most don't.
WordPress is actually more up to date compared to other CMSsWhile this practice has died down, it existed for many years, which explains the large number of vulnerable WordPress websites that can't be updated with ease.
In fact, Sucuri says that, despite the grim situation, WordPress is actually in a good position. The security firm says that, out of all the compromised websites, only 56 percent of WordPress sites were running outdated WordPress core versions.
For Joomla, this number was 85 percent, for Drupal it was 81 percent, while for Magento, where the upgrade process is a pain in "you know where," this was 97 percent.
"These statistics talk to the challenges website owners face, regardless of size, business, or industry. Website owners are unable to keep up with the emerging threats. As well, the guidance they receive to 'stay current' or 'just update' is not enough," Sucuri explained. "Website owners are turning to other technologies, like Website Application Firewall (WAF), to give themselves and their organizations the time they require to more efficiently respond to the threats by way of virtual patching and hardening techniques at the edge."
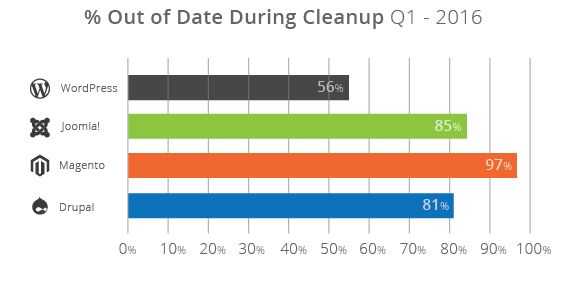
Percentage of oudated versions per CMS platform
Source: A Quarter of All Hacked WordPress Sites Can Be Attributed to Three Plugins
No comments:
Post a Comment